Prefectures of Japan. It consists of 8 areas, one “To” and one “Dou”, two “Fu”, and 43 “Ken”.

Geographical Features of the Japanese Archipelago
The Japanese archipelago consists of arc-shaped islands located on the Pacific side of East Asia. It comprises four main islands—Hokkaidou (Hokkaido), Honshuu (Honshu), Shikoku, and Kyuushuu (Kyushu) —along with over 6,000 smaller islands.
With a total area of approximately 378,000 square kilometers, about 70% of Japan’s territory is mountainous. Majestic mountains such as the Japanese Alps and Mount Fuji (3,776m) form part of the “Pacific Ring of Fire,” bringing abundant natural blessings to the country.
Surrounded by ocean on all sides, Japan’s coastline extends approximately 29,751km, providing diverse marine resources. The beautiful coastlines and hot springs are also important tourism assets.
The climate varies by region, with subarctic conditions in the north, temperate in the central and southern areas, and subtropical in Okinawa. Japan enjoys four distinct seasons, each offering unique natural landscapes to appreciate.
Due to its elongated north-south geography, Japan is blessed with diverse food cultures. These range from Hokkaidou (Hokkaido)’s fresh seafood and dairy products, Touhoku (Tohoku)’s rice and fruits, traditional Kansai cuisine, Kyuushuu (Kyushu)’s pork dishes, to Okinawa’s unique ingredients and cooking methods. The culture of cherishing seasonal ingredients has also emerged from this geographical diversity.

Hokkaidou(Hokkaido) / Touhoku(Tohoku)
Located in northern Japan, characterized by vast nature and cool climate. Features magnificent mountains, beautiful lakes, and expansive plains. Known for high-quality agricultural products like rice, apples, and cherries. Heavy snowfall in winter makes it popular for skiing and winter sports. Preserves many unique cultural traditions and festivals.
Hokkaidou (Hokkaido)

Aomori – ken
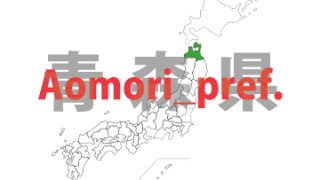
Iwate – ken
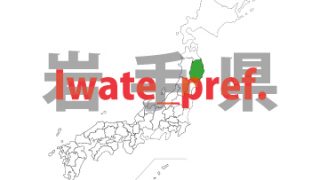
Akita – ken

Miyagi – ken

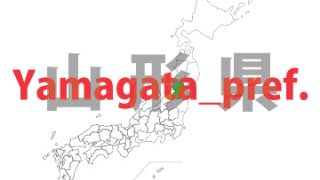
Yamagata – ken
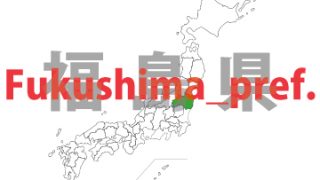
Fukushima – ken

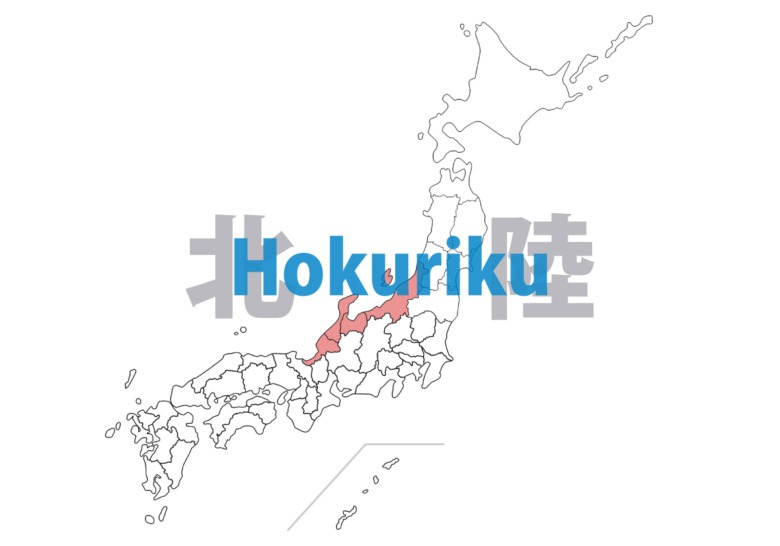
Hokuriku
Facing the Sea of Japan, features abundant snowmelt water and fertile plains. Known for heavy snow in winter and beautiful mountain and coastal landscapes. Famous rice-growing area and renowned for sake production. Home to traditional crafts like Kaga Yuuzen dyeing and Wajima lacquerware. Numerous hot springs are popular tourist attractions.
Niigata – ken

Toyama – ken

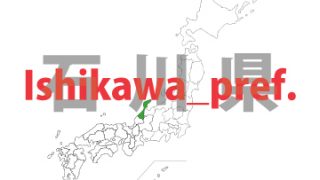
Ishikawa – ken
Fukui – ken


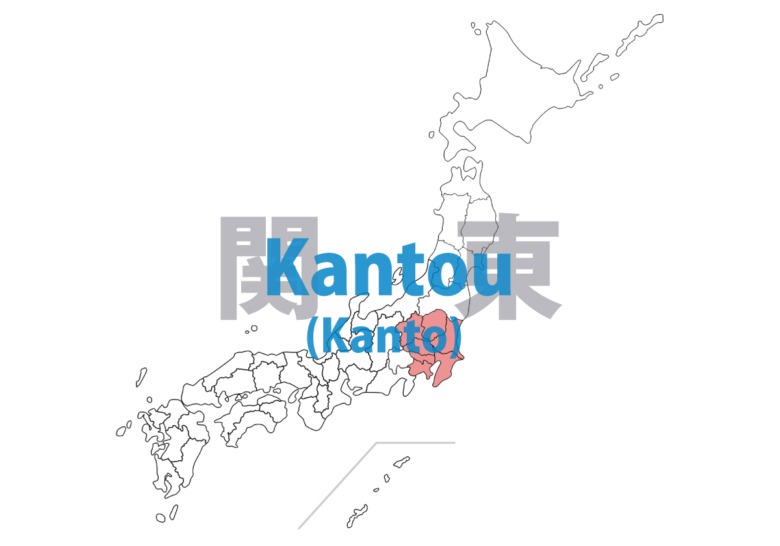
Kantou(Kanto)
Japan’s political and economic center, developed around the vast Kantou (Kanto) Plain. The Toukyou (Tokyo) metropolitan area is one of the world’s largest urban concentrations and a hub for cutting-edge technology and culture. Diverse natural environments including satoyama (rural landscapes) and coastlines. Temperate climate with distinct seasons supports diverse agricultural production.
Ibaraki – ken

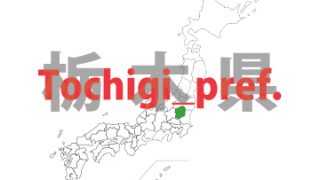
Tochigi – ken
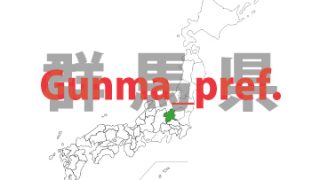
Gunma – ken
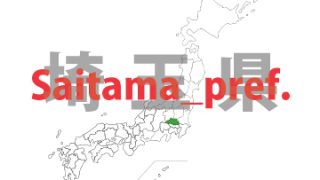
Saitama – ken
Chiba – ken

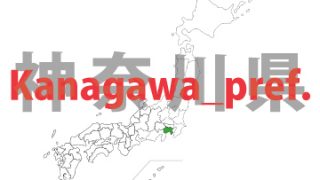
Kanagawa – ken
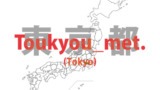
Toukyou (Tokyo) – to

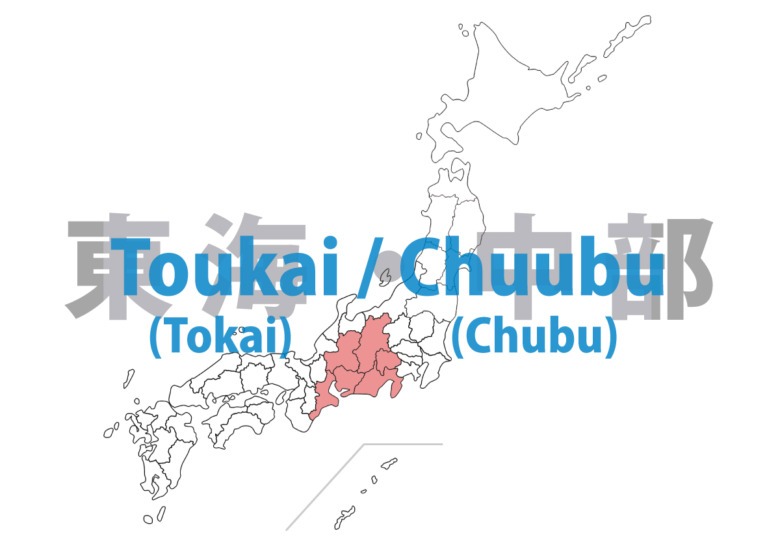
Toukai(Tokai) / Cuubu(Chubu)
Located in central Japan with both Pacific and Japan Sea climate influences. Consists of Japanese Alps mountain ranges and fertile plains. Developed manufacturing sector centered on the automotive industry. Many preserved traditional castle towns and post stations. Features distinctive regional cuisines.
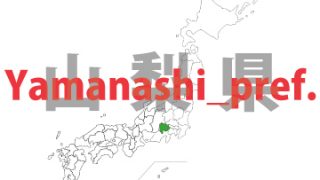
Yamanashi – ken
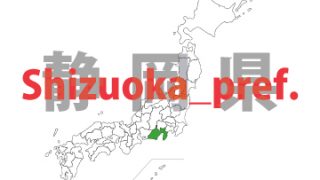
Shizuoka – ken
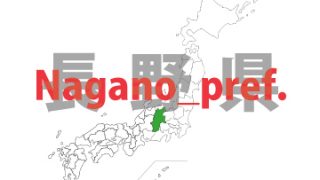
Nagano – ken
Gifu – ken

Aichi – ken

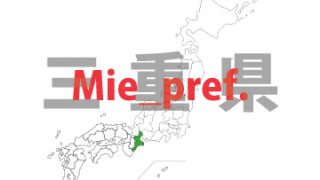
Mie – ken

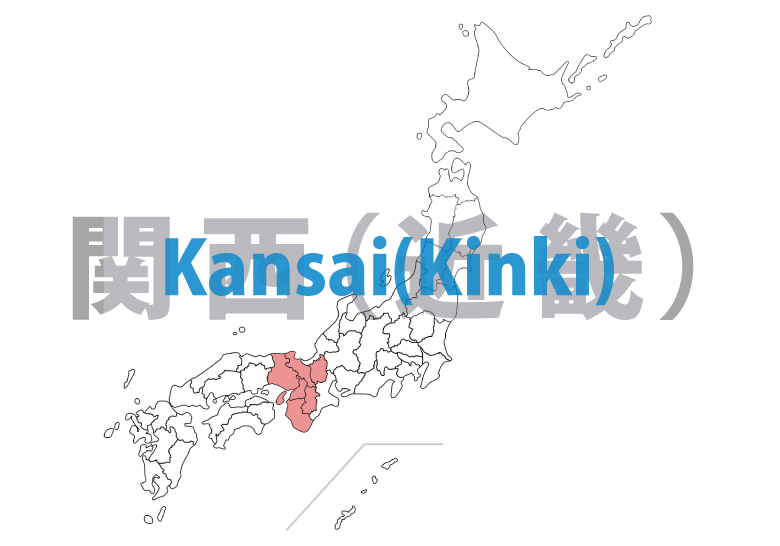
Kansai-Kinki
Birthplace of ancient Japanese culture, with numerous historical buildings and cultural heritage sites centered in Kyouto (Kyoto) and Nara. Oosaka (Osaka) developed as a commercial center with unique food and entertainment culture. Attractive natural environments from the Seto Naikai (Seto Inland Sea) and Wakasa Bay to the Hira mountain range.
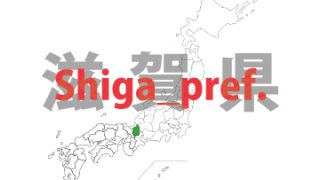
Shiga – ken
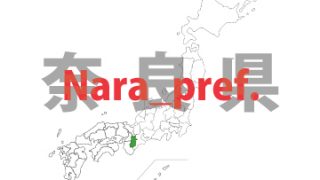
Nara – ken
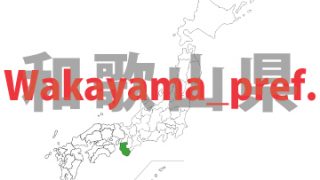
Wakayama- ken
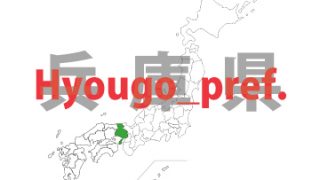
Hyougo(Hyogo)- ken
Kyouto(Kyoto)- fu

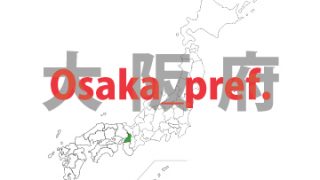
Oosaka(Osaka)- fu

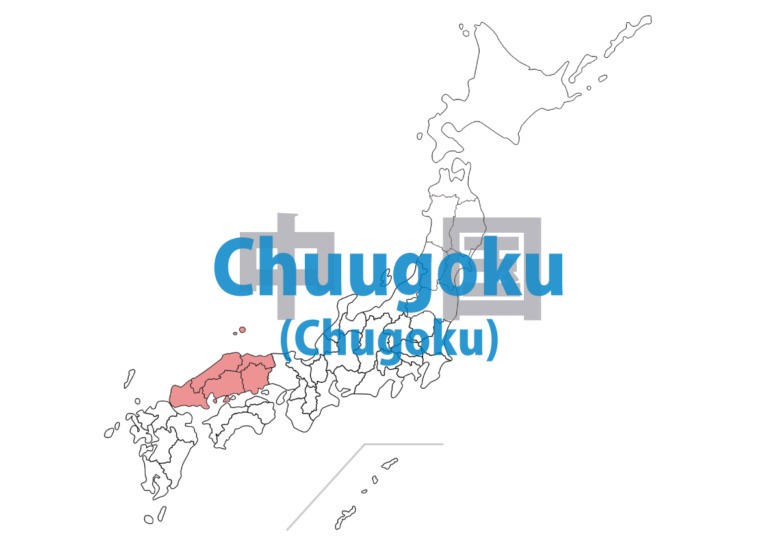
Chuugoku(Chugoku)
Western Honshuu (Honshu) surrounded by contrasting seas: Sea of Japan to the north and Seto Inland Sea to the south. The Chuugoku (Chugoku) mountain range divides the region, creating different climates and cultures. The Seti Naikai (Seto Inland Sea) side enjoys a mild climate, with developed shipbuilding and steel industries. Important cultural and historical sites include Hiroshima’s Genbaku (Atomic bomb) Dome and Izumo Taisha shrine.
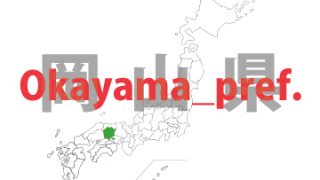
Okayama – ken
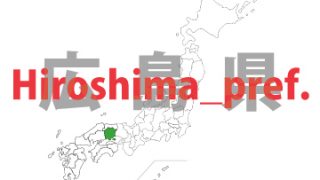
Hiroshima – ken
Tottori – ken

Shimane – ken

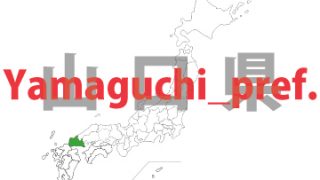
Yamaguchi – ken

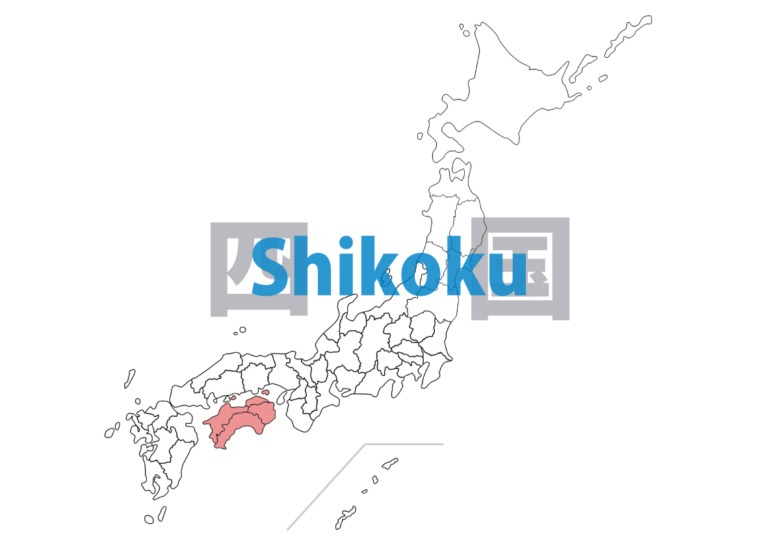
Shikoku
Japan’s smallest major island, surrounded by sea with the Shikoku mountain range running through its center. The warm climate supports citrus cultivation, especially in Ehime Prefecture. The “Shikoku Pilgrimage” route connecting 88 temples is an important cultural heritage site and tourist attraction.
Kagawa – ken
Tokushima – ken
Ehime – ken

Kouchi(Kochi)- ken


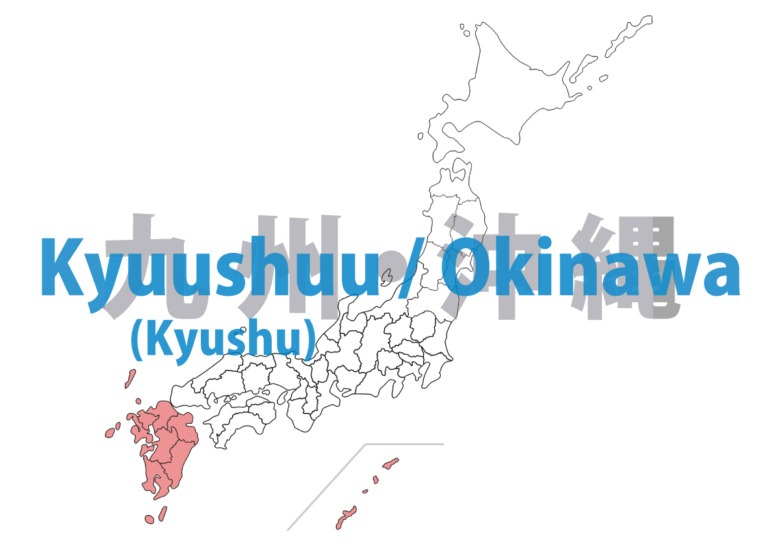
Kyuushuu (Kyushu) / Okinawa
Kyuushuu (Kyushu) enjoys a warm climate and rich volcanic soil, supporting thriving agriculture. Active volcanoes like Mt. Aso and Sakurajima provide numerous hot springs. Nagasaki and Kagoshima historically served as important gateways to foreign countries. Subtropical Okinawa developed the unique Ryuukyuu (Ryukyu) culture, with beautiful coral reefs that attract tourists.
Fukuoka – ken
Saga – ken

Nagasaki – ken

Ooita(oita) – ken

Kumamoto – ken
Miyazaki – ken

Kagoshima – ken

Okinawa- ken